The Virgo interferometer
The IJCLab “Gravitational Waves” group is among the founders of the Virgo Collaboration in the 1990s.
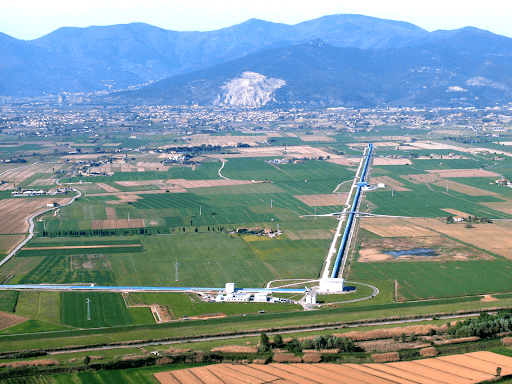
Virgo is a gravitational-wave detector. It is a giant laser interferometer on the ground, whose mirrors are suspended and under vacuum. It has been designed and built, and is now operated, by an international collaboration that counts several hundred members from more than 100 European research institutions.
The Virgo detector, located at the European Gravitational Observatory (EGO) in Cascina (near Pisa), Italy, is part of a global network that currently counts four instruments: Virgo, plus the two US-based LIGO detectors, Hanford (WA), Livingston (LA) and the KAGRA detector, built underground in Japan. The LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA (LVK) network has now detected dozens of gravitational-wave signals since 2015 and more are expected in the future.
Historical discoveries
Information about the Virgo detector, about gravitational wavs and the associated science and about the LVK network, is available on public webpages. The list of LVK publications is available here. Among the main discoveries / scientific results one can list:
- GW150914: the first gravitational-wave event ever detected, the merger of a binary black hole system.
- GW170814: the first 3-detector gravitational-wave detection — another binary black hole merger.
- GW170817: the first binary neutron star merger ever detected whose electromagnetic counterpart has been detected and localized by many telescopes worldwide, leading to the birth of multi-messenger astronomy with gravitational waves.
- GWTC-1: the LIGO-Virgo catalog of transient sources from 2015-2017 — covering the “Observing Runs” O1 (2015/09 -> 2016/01) and O2 (2016/11 -> 2017/08) .
- GWTC-2: the LVK catalog of transient sources up to the first part of the O3 run — O3a: 2019/04 -> 2019/10).
More information about these results, such as the associated public datasets, can be found on the Gravitational Wave Open Science Center (GWOSC).









