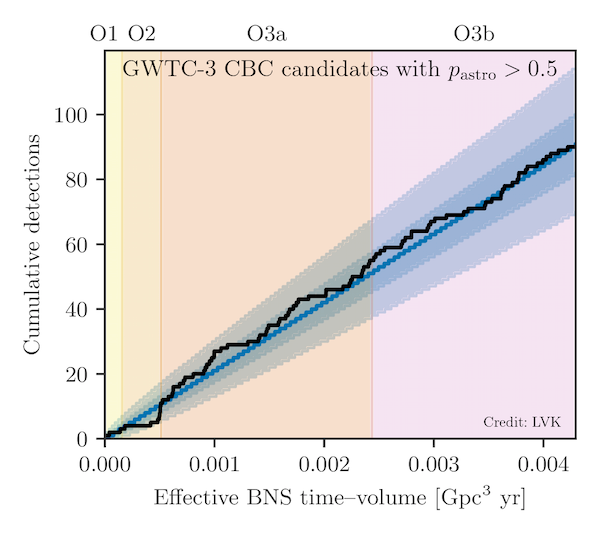
The LIGO and Virgo detectors have observed 35 new gravitational-wave events, between November 2019 and March 2020, during the second half of the third observing run (O3b). The total number of detected gravitational-wave signals is now close to 100.

The LIGO and Virgo detectors have observed 35 new gravitational-wave events, between November 2019 and March 2020, during the second half of the third observing run (O3b). The total number of detected gravitational-wave signals is now close to 100.